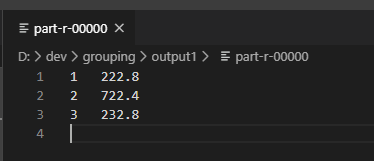
排序,是 MapReduce 中最重要的操作之一。默认的排序方式是 字典排序,且实现此排序的方式是 快速排序。
MapTask 和 MapReduce 均会对数据按照 key 进行排序,该操作属于 Hadoop 的默认操作。任何程序中的数据均会被排序,不论逻辑上是否需要。
排序概述
对于 MapTask
它会将处理的结果暂时放到 环形缓冲区 中,当缓冲区的使用率达到一定的阈值之后,再对缓冲区中的数据进行一次快速排序,并将这些有序数据溢写到磁盘上,而当数据处理完毕后,它会对磁盘上的文件进行 归并排序。
对于 ReduceTask
它从 每个 MapTask 上远程拷贝相应的数据文件,如果文件大小超过一定阈值,则溢写到磁盘上,否则存储到内存。
如果磁盘上的文件数据达到一定阈值,则进行一次 归并排序,以生成一个更大的文件。
如果内存中文件大小或数目,达到一定阈值,则进行一次 合并,将数据溢写到磁盘上。
当所有数据拷贝完成后,ReduceTask 统一对内存和磁盘上的数据进行一次 归并排序。
排序的分类
部分排序
MapReduce 根据输入记录的键,对数据集排序,保证输出的每个文件,内部有序
全排序
最终输出结果只有一个文件,且文件内部有序。实现方式是:只设置一个 ReduceTask。但是该犯法在处理大型文件是,效率极低,完全丧失了 MapReduce 所提供的并行架构。
辅助排序(GroupingComparator 分组)
在 Reduce 端对 key 进行分组。应用于:在接收的 key 为 bean 对象时,想让一个或几个字段相同(并不是全部字段相同)的 key 进入到同一个 Reduce 方法时,可以使用分组排序
二次排序
在自定义排序过程中,如果 compareTo 中的条件为两个,即为二次排序。
自定义排序(全排序)
bean 对象作为 key 传输,需要实现 WritableComparable 接口,重写 compareTo 方法。
需求:使用之前 序列化实例 的结果作为 输入数据,期望输出:按照总流量倒序排序。
实现
Bean
序列化实例 中的 FlowBean 类,实现 WritableComparable 接口,重写 compareTo 方法
1 | public int compareTo(FlowBean flowBean) { |
Mapper
1 | private FlowBean flowBean = new FlowBean(); |
Reducer
1 |
|
Driver 省略,测试结果
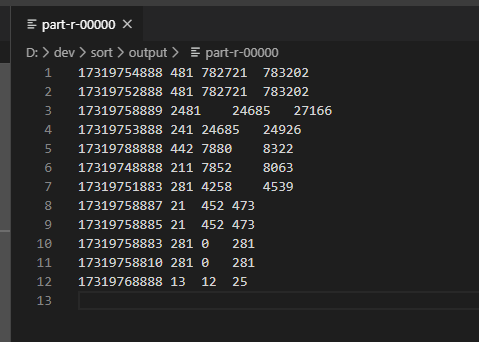
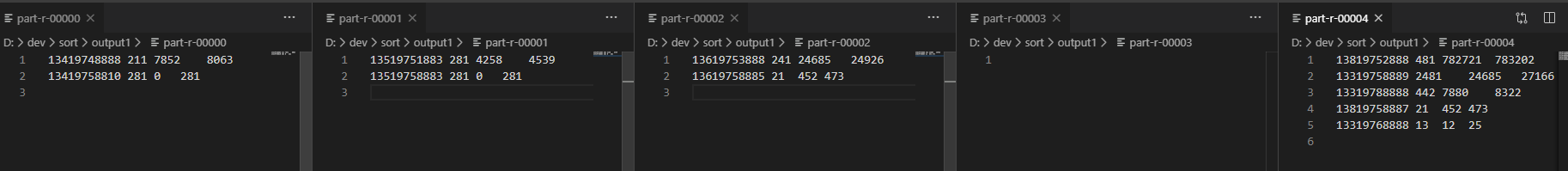
区内排序
需求:使用 输入数据,期望输出:根据手机号的前三位不同,分成不同的文件,并在每个文件中,按照总流量倒序输出。
在上一例全排序的基础上,增加一个分区操作。
1 | public class FlowBeanPartitioner extends Partitioner<FlowBean, Text> { |
查看结果
合并
Combiner 是 MapReduce 程序中 Maper 和 Reducer 之外的一种组件
Combiner 是父类是 Reducer
Combiner 与 Reducer 的区别在于运行的位置:Combiner 是在每个 MapTask 所在的节点运行;Reducer 是接收全局所有 Mapper 的输出结果
Combiner 的意义是对每个 MapTask 的数据进行局部汇总,以减小网络的传输量
应用前提:不能影响最终的业务逻辑(Combiner 输出的 KV,应该与 Reducer 的输入 KV 类型对应)
自定义 Combiner
需求: 使用 输入数据,进行 局部汇总,以减小网络传输量。
期望输出:分隔单词,局部汇总每个单词的数量
以 WordCount 实例为例
原始的 WordCount 的控制台输出为:
1 | Map-Reduce Framework |
方案 1
自实现一个 Combiner,并在 Driver 中注册。
1 | public class WordCountCombiner extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> { |
1 | job.setCombinerClass(WordCountCombiner.class); |
测试运行:
1 | Map-Reduce Framework |
方案 2
直接将之前的 Reducer 作为 Combiner 即可。job.setCombinerClass(WordCountReducer.class);
辅助排序
GroupingComparator,对 Reducer 阶段的数据根据某一个或几个字段进行分组。
分组排序步骤:
自定义排序类,继承 WritableComparator
从学 compare 方法
创建一个构造,将比较对象传给父类
Demo
根据订单 输入数据,进行分组,并找出每笔订单中最贵的商品
实现步骤:
- 利用 “订单 id、成交金额” 作为 key,可以将 Map 阶段读取到的订单数据按照 id 进行排序。如果 id 相同,再根据金额降序,然后发送到 Reducer
- 在 Reducer 利用 GroupingComparator 将订单相同的 KV 聚合成组,然后取第一个即可。
创建一个 Bean,用于存储订单信息
1 | public class OrderBean implements WritableComparable<OrderBean> { |
Mapper
1 | public class OrderMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, OrderBean, NullWritable> { |
Reducer
1 | public class OrderReducer extends Reducer<OrderBean, NullWritable, OrderBean, NullWritable> { |
Driver 省略
结果
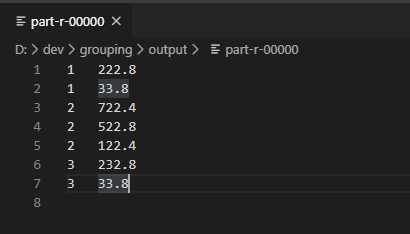
开始分组排序
在得到了结果后,可以看到,现在的结果确实是不同订单的,在一起显示,且是按照倒序排列的。只不过,没有进行分组,没有完成只输出第一条。在此基础上,开始进行辅助分组排序。
1 | public class OrderGroupingComparator extends WritableComparator { |
Driver
1 | job.setGroupingComparatorClass(OrderGroupingComparator.class); |
运行测试