Spring Batch – 一个基于 Spring 架构的批处理框架
什么是批处理
在现代企业应用当中,面对复杂的业务以及海量的数据,除了通过庞杂的人机交互界面进行各种处理外,还有一类工作,不需要人工干预,只需要定期读入大批量数据,然后完成相应业务处理并进行归档。这类工作即为“批处理”。如:银行、移动、电信等公司需要每个月的月底统一处理用户的剩余金额、流量、话费等,这是一个很大的工程。如果全部使用人工操作的话,可能几个月都统计不了,这时就需要一套已经制定好规则的处理方案,按照制定好的方案,程序进行自动处理。
从上面的描述可以看出,批处理应用有如下几个特点:
- 数据量大,少则百万,多则上亿的数量级。
- 不需要人工干预,由系统根据配置自动完成。
- 与时间相关,如每天执行一次或每月执行一次。
同时,批处理应用又明显分为三个环节:
- 读数据,数据可能来自文件、数据库或消息队列等
- 数据处理,如电信支撑系统的计费处理
- 写数据,将输出结果写入文件、数据库或消息队列等
因此,从系统架构上,应重点考虑批处理应用的事务粒度、日志监控、执行、资源管理(尤其存在并发的情况下)。从系统设计上,应重点考虑数据读写与业务处理的解耦,提高复用性以及可测试性。
SpringBatch 的业务场景
- 周期性的提交批处理
- 把一个任务并行处理
- 消息驱动应用分级处理
- 大规模并行批处理
- 手工或调度使用任务失败之后重新启动
- 有依赖步骤的顺序执行(使用工作流驱动扩展)
- 处理时跳过部分记录(错误记录或不需要处理的记录)
- 成批事务:为小批量的或有的存储过程/脚本的场景使用
SpringBatch 集成操作
### Spring 官方推荐使用 SpringBoot 作为 SpringBatch 的容器框架。
SpringBoot 作为 Spring 官方提供的一款轻量级的 Spring 全家桶整合框架,基于 习惯优于配置 的特点,有以下几个重点特征:
- 基本没有或极少的配置即可启动 Spring 容器
- 创建独立的Spring应用程序
- 嵌入的Tomcat,无需部署WAR文件
- 简化Maven配置
- 自动配置Spring
- 提供生产就绪型功能,如指标,健康检查和外部配置
- 绝对没有代码生成并且对XML也没有配置要求
SpringBoot 集成 SpringBatch 简单实例(使用 IDEA)
创建一个 SpringBoot 项目
File –> new –> project –> Spring Initialzer
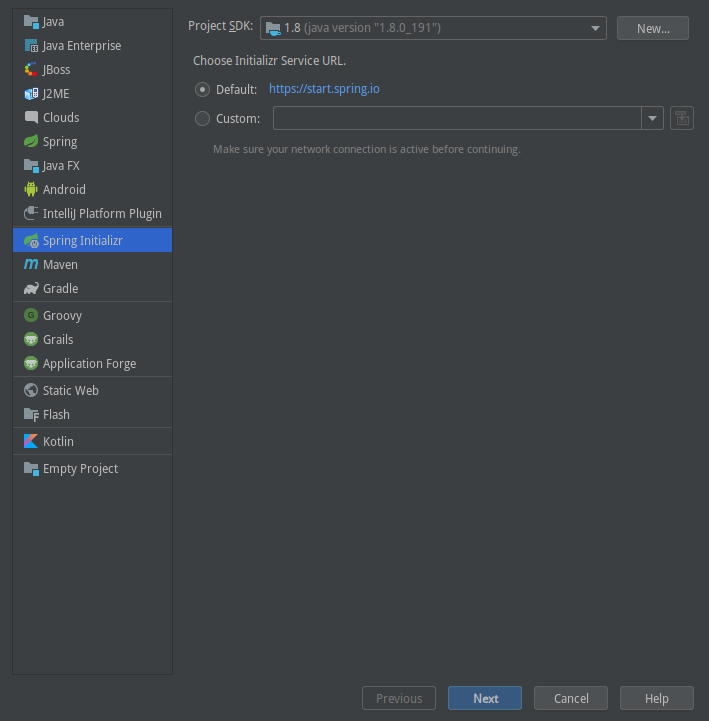
填写 groupId、artifactId
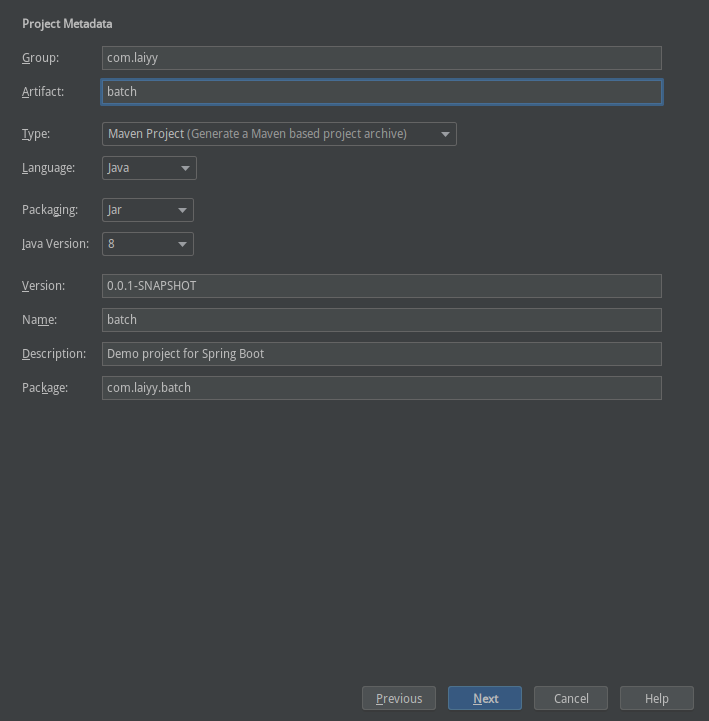
选择需要的依赖(由于是简单实例,所以只需要 batch 的依赖即可)
完整 pom.xml 文件
1 |
|
开始第一个简单示例
demo 示例编码步骤
- 引入 JobBuilderFactory、StepBuilderFactory,用于创建任务、任务执行的步骤
- 使用 JobBuilderFactory 创建一个任务
- 使用 StepBuilderFactory 创建这个任务要执行的步骤
- 启动项目,查看运行结果
需要注意的地方:
- 将所有操作在一个类中完成,便于理解代码
- 需要在这个类上加入 @Configuration、@EnableBatchProcessing 注解
- 直接启动主进程即可在控制台查看到运行结果
注解 @Configuration 等价于在 spring-context.xml 中声明一个 <bean> 节点
注解 @EnableBatchProcessing 用于告诉 Spring 容易自动装配 SpringBatch 相关默认配置
具体代码:
1 | /** |
验证运行结果
启用 Application 主进程,查看控制台,发现报错如下:
1 | Error starting ApplicationContext. To display the conditions report re-run your application with 'debug' enabled. |
错误原因:
SpringBatch 运行任务、Step 的时候,会进行持久化(可能是内存中、或者是数据库中,默认是数据库),所以再次我们需要引入一个数据库。作为一个 示例程序,引入内存级数据库 h2 即可
需要在 pom.xml 中加入如下配置:
1 | <dependency> |
再次启动项目,查看控制台,可以看到控制台打印信息如下
1 | . ____ _ __ _ _ |
此时可以看到,我们在 Tasklet 中输出的字符串成功打印在了控制台中,证明 SpringBatch 的简单示例启动、验证成功。