此前,完成了一个基础的完全分布式集群,并且使用 Java 程序代码实现测试连通了 Hadoop 集群,且在 HDFS 中创建了一个文件夹。由此开始学习 Hadoop 的一些 Java API 操作。
API 操作通用方法
1 |
|
HDFS API 操作
文件上传
1 |
|
将 $HADOOP_HOME$/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml 文件,拷贝到 Java 程序的 /resources 文件夹下,并修改为:
1 | <configuration> |
注释掉程序中设置副本数的代码,再次上传文件,查看上传后文件副本数
结论:
1、如果程序中未设置副本数,且不存在 hdfs-site.xml 文件,则以 Hadoop 中设置的 hdfs-site.xml 中的副本数优先
2、如果程序中未设置副本数,存在 hdfs-site.xml 文件,以程序中的 hdfs-site.xml 中的副本数优先
3、如果程序中设置了副本数,且存在 hdfs-site.xml,以程序中设置的副本数优先
4、如果程序中设置了副本数,且不存在 hdfs-site.xml,以程序中设置的副本数优先
即:Java 程序 > resources 中的 hdfs-site.xml > hadoop 中的 hdfs-site.xml > hadoop 默认的副本数
文件下载
1 |
|
文件删除
1 |
|
文件改名
1 |
|
查看文件详情
可以查看文件名称、权限、长度、块信息等
1 | public void testListFiles() throws IOException { |
返回值:
1 | // 文件信息 |
判断是否是文件夹
1 |
|
HDFS I/O 流操作
文件上传
1 |
|
文件下载
1 |
|
HDFS 文件定位读取
先往 HDFS 中上传一个大于 128M 的文件,在管理器中查看一下文件的分块大于1。
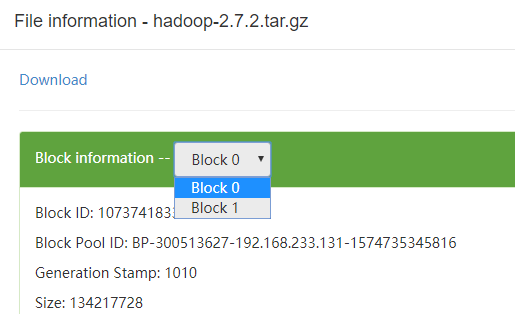
可见当前文件分为了两块存储。如果此时进行下载,会将两块数据合并起来下载。但如果只想要下载其中的一部分,现在的下载方法无法实现。
1 | // 只读取第一块的数据 |
HDFS 读写数据流程
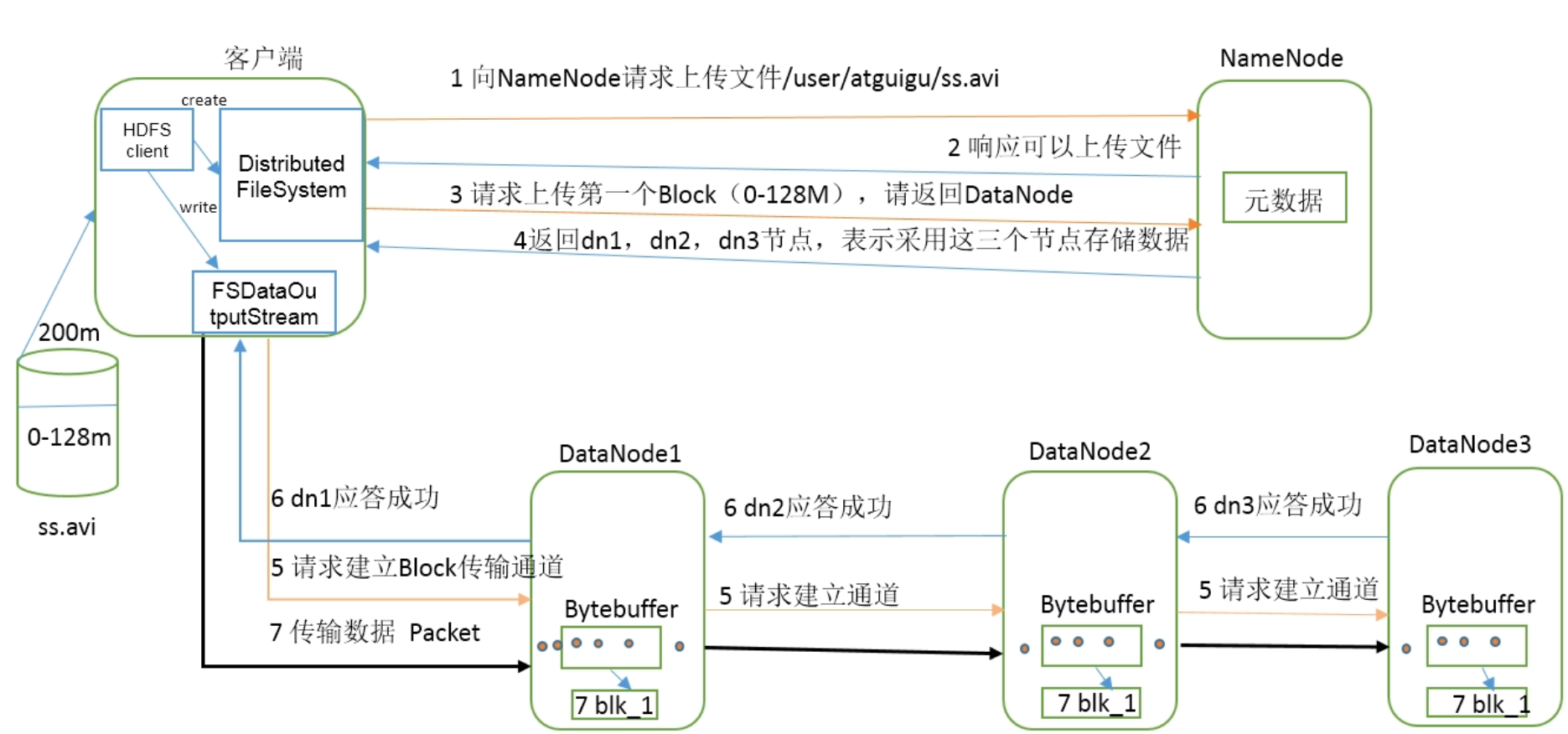
HDFS 写数据流程
- 使用 FileSystem.get 创建一个
分布式文件系统客户端,向 NameNode 请求上传文件 - NameNode 检查 HDFS 中是否有待上传的文件(根据路径、文件名判断),如果存在该文件,则报错
文件已存在 - 如果 NameNode 检查后,HDFS 没有待上传的文件,则开始响应上传文件
- 请求上传第一个 block(根据配置不同,block 大小也不同),此时会向 DataNode 请求,由 DataNode 决定可以上传到哪几个节点上
- DataNode 返回可以上传的节点(判断条件:节点距离,负载)
- FileSystem 创建输出流(FsDataOutputStream),与 DataNode 建立通道(串行)
- DataNode 应答,所有可上传节点应答成功后,开始传输数据
- 所有数据传输完成后,通知 NameNode
节点距离计算
节点距离:两个节点到最近的共同祖先的距离总和
HDFS 写数据过程中,NameNode 会选择距离上传数据最近距离的 DataNode 接收数据,此时需要计算节点距离。
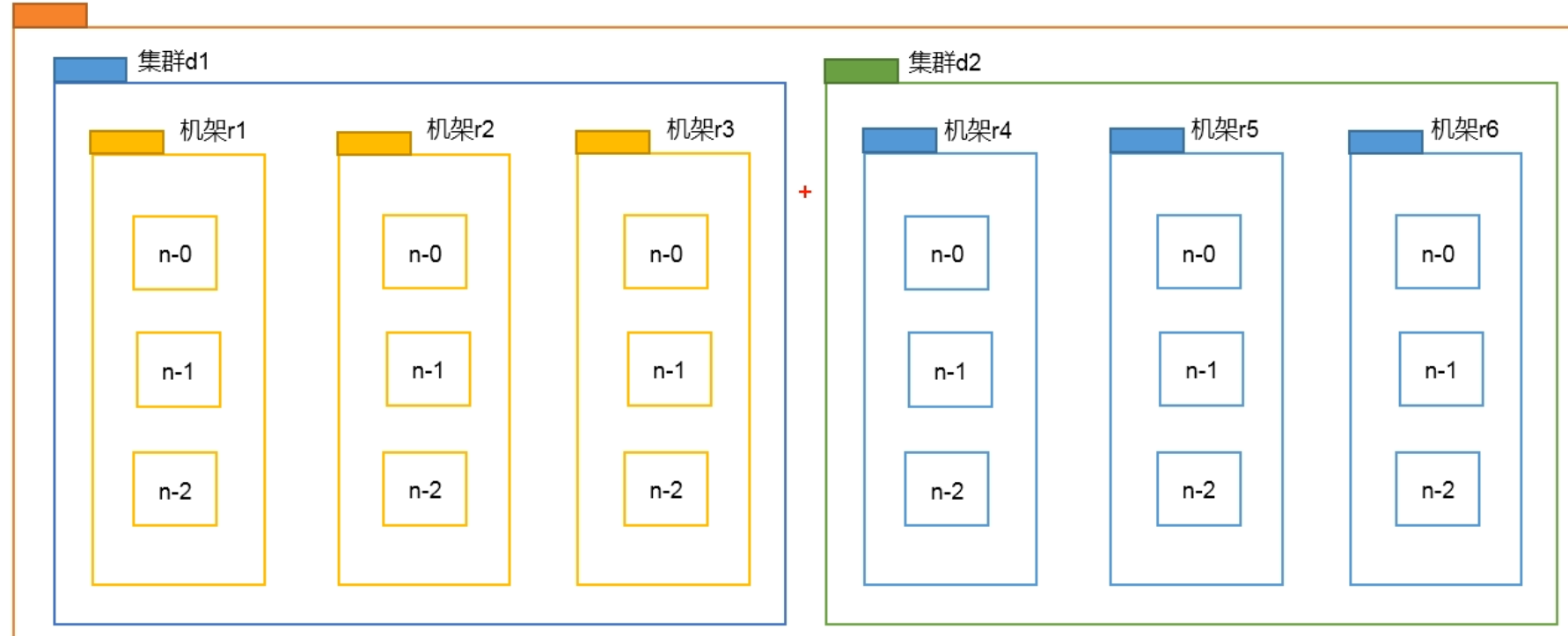
(d1-r1-n0, d1-r1-n0),由于这两个节点在同一个服务器上,此时距离为 0。即:同一节点上的进程距离为 0。
(d1-r1-n1, d1-r1-n2),由于这两个节点都在同一个机架上,所以 n1、n2 的共同祖先都为 r1,此时距离为 1+1=2
(d1-r2-n0, d1-r3-n2),这两个节点在同一个集群的不同机架上,即这两个节点的共同祖先为 d1,节点到集群还需要经过机架,所以这两个节点到共同祖先的距离都为 2,则节点距离为 2+2=4
(d1-r2-n1, d2-r4-n1),这两个节点也不在同一个集群,则共同祖先为最外围的“网段”,此时每个节点到“网段”的距离都为 3,所以节点距离为 3+3=6
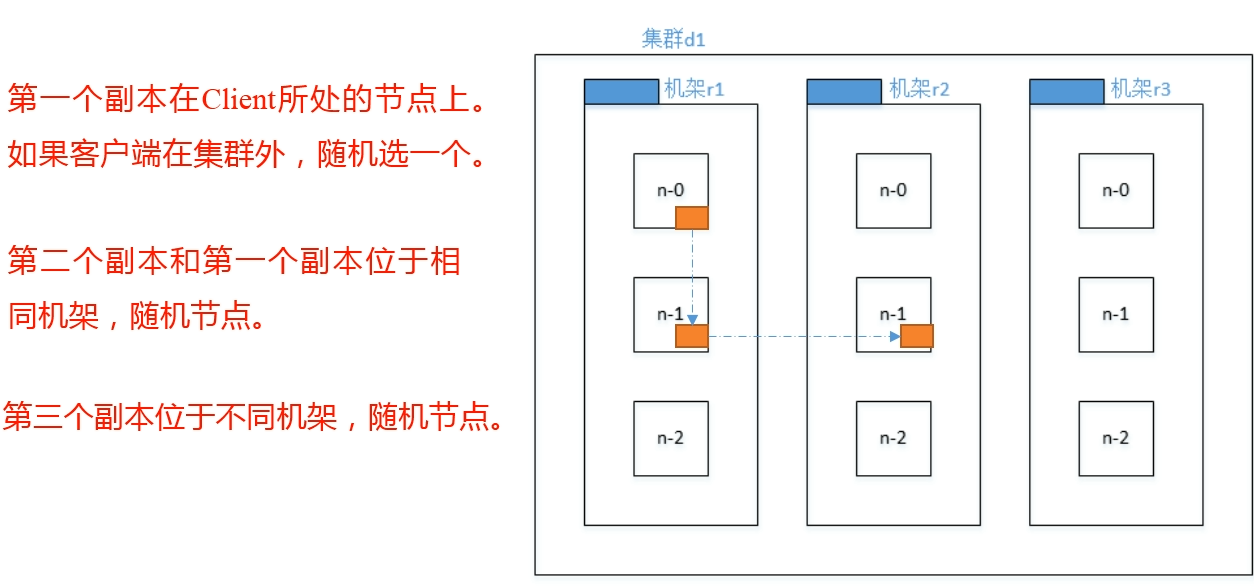
机架感知(副本存储节点选择)
默认情况下,当副本数为 3 时,HDFS 的副本策略是在 本地机架 上的一个节点放置一个副本,在 本地机架的另外一个节点 上放置一个副本,最后再 另外一个机架 的不同节点上防止最后一个副本。
老版本的 hadoop 正好相反,是在 本地机架 上放置一个副本,在 另外一个机架 上放置 2 个副本。
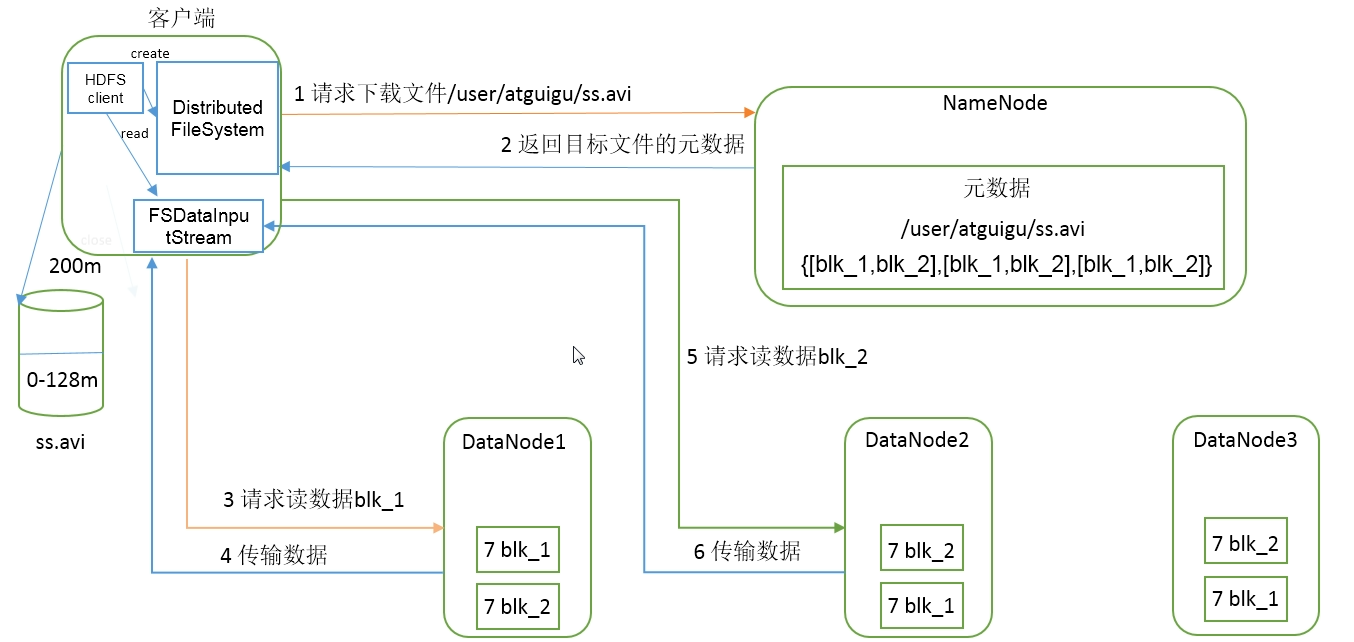
HDFS 读数据流程
- 客户端请求下载文件(向 NameNode 发送请求)
- NameNode 返回目标文件元数据
- 客户端创建输入流
- 客户端请求读取数据(根据距离决定从那个 DataNode 获取数据)
- DataNode 传输数据